Alzheimer’s is not just random memory loss associated with aging. From a scientific perspective, it is a series of complex and negative biochemical reactions occurring silently for decades before the first symptoms emerge. At DOIT Scientific, we believe that understanding the “enemy” at the cellular level is the essential first step to taking early action and sustainably protecting cognitive health.
Below is an in-depth analysis of the two primary culprits behind neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s:
1. Amyloid-beta Plaques: The “Waste” Blocking Neural Communication
In a healthy brain, fragments of Amyloid-beta protein are naturally broken down and eliminated. However, in Alzheimer’s patients, this process is disrupted:
- Nature: These proteins accumulate abnormally, clumping together to form hard plaques in the extracellular spaces between neurons.
- Mechanism of Harm: These plaques act as physical barriers, blocking the Synapses—the critical junctions where signal transmission occurs between neurons.
- Consequence: Once communication is paralyzed, the brain regions responsible for learning and memory begin to weaken. These represent the earliest signs of the disease that are often overlooked.
2. Tau Protein Tangles: The Collapse of Intracellular Transport
While Amyloid-beta attacks from the outside, Tau protein causes destruction from within the cell:
- Nature: In a normal state, Tau proteins help stabilize the “tracks” (microtubules) that transport nutrients within neurons. When chemically modified (phosphorylated into pTau), they lose their original shape and twist into tangles.
- Mechanism of Harm: The formation of these tangles causes the internal “railway” system for nutrient transport to collapse entirely. Neurons are cut off from their nutrition source, leading to atrophy and mass cell death.
- Consequence: This is the direct cause of the loss of reasoning, behavioral control, and eventually, severe memory loss.
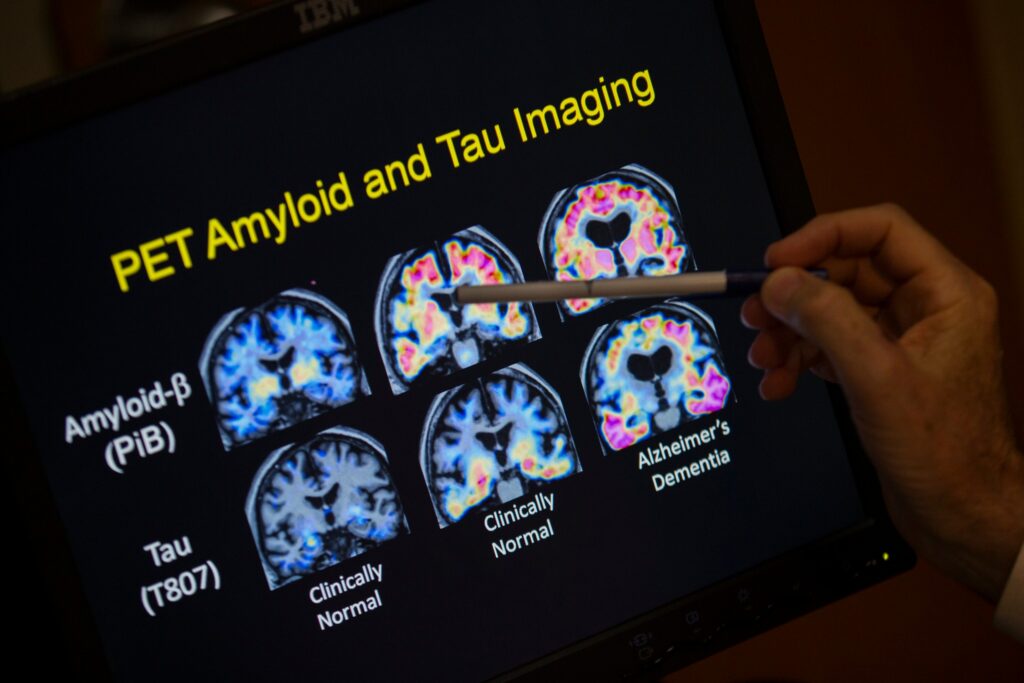
Actionable Message: The Importance of Biomarker Screening
Modern science has proven that waiting for clinical symptoms to appear is often too late for effective intervention. The presence of Amyloid-beta and pTau in the body can be detected very early through Biomarker screening.
Identifying these indicators based on scientific evidence is the “golden key” that allows you and your family to proactively establish a brain health care plan, slowing disease progression and protecting long-term quality of life.

![[STRATEGIC ANALYSIS] THE ALZHEIMER’S CRISIS: A GLOBAL HEALTHCARE AND ECONOMIC CHALLENGE](https://doitvn.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/571335627_1391195439675082_3276405501578917534_n-440x300.jpg)